
DAC-LAT: A New Tool for Navigating the Complexities of Direct Air Capture
Published by Todd Bush on March 3, 2025
Achieving Net Zero and the Role of Direct Air Capture
As the world grapples with climate change, the concept of achieving net zero emissions by 2050 and net negative thereafter has emerged as a cornerstone of climate policy. Central to this goal is using carbon dioxide removal (CDR) to balance residual emissions by removing an equivalent amount of CO₂ from the atmosphere.
While there is no one existing definition for residual or hard-to-abate emissions, they are typically those that are technically challenging or economically unfeasible to mitigate at the source. Sectors such as aviation, agriculture, or the remaining emissions leftover after applying carbon capture and storage (CCS) to cement production come to mind. Another use of carbon removals is to deliver net negative emissions, whereby more carbon is removed from the atmosphere than is added—another goal of the EU post-net zero.
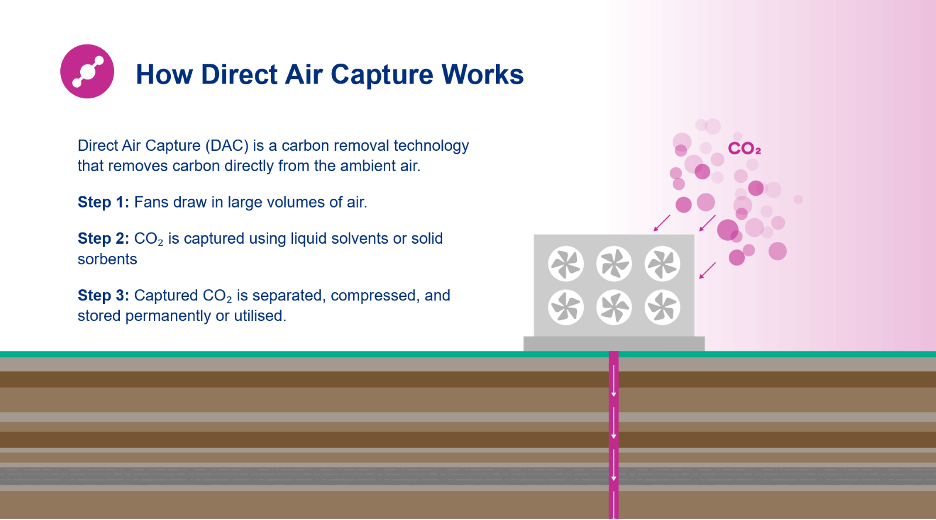
One such set of technologies to deliver carbon removals is direct air capture (DAC). DAC extracts CO₂ directly from ambient air using chemical processes. Projects primarily employ either liquid solvents or solid sorbents to capture CO₂, which is then compressed and transported to storage or utilization. When paired with permanent storage methods like geological sequestration or mineral carbonation, DAC becomes a carbon dioxide removal solution known as DACS.
>> In Other News: Carbon TerraVault and National Cement Sign MOU for California’s First Net Zero Cement Facility
How Does DAC Capture CO₂?
There are many different variants of DAC technology under development, but two leading technology types are currently being deployed at relatively large scales (capturing tens of thousands of tonnes of CO₂ annually or more):
Solid Sorbent DAC (S-DAC): Air is passed over solid materials that chemically bind with CO₂. The sorbent is then heated to a temperature below 100ºC to release the captured CO₂ for storage.
Liquid Solvent DAC (L-DAC): Air is exposed to a liquid solution that absorbs CO₂ and chemically converts it to solid carbonate pellets. A high-temperature kiln (~900ºC) is then used to break down the carbonate and release pure CO₂.
While DAC is energy-intensive, its flexibility, scalability, and modularity make it a promising tool for carbon removal. Moreover, the ability to verify and monitor negative emissions with precision adds to its appeal.
However, not all countries have the available resources to make efficient use of DACS, as the process can be highly energy-intensive. This means that considering the greenhouse gas intensity of its energy inputs is vital to determine its ability to deliver net removals. That’s where our new Direct Air Capture Lifecycle Analysis Tool (DAC-LAT) comes in.
The Direct Air Capture Lifecycle Analysis Tool
What is DAC-LAT?
DAC‐LAT is an interactive online tool that lets you estimate the net CO₂ removal achieved by a DAC facility. Here’s how it works:
Interactive input selection: Users begin by choosing the Global Warming Potential (GWP) time horizon and selecting which DAC technology to evaluate. The tool currently allows users to choose between the two archetypal DAC methods: solid sorbents and liquid solvents.
Users can also set the plant’s operational lifetime, the annual operational time fraction, and estimate the cost of energy inputs by entering unit prices for electricity and heat.
* National and regional electricity grids
* Natural gas supply chains
* A dedicated renewable or fossil energy source
* Future projections of grid carbon intensity
Comprehensive Emissions Breakdown
DAC‐LAT calculates emissions from each stage of the DAC value chain—from the energy consumed during capture and the construction of the facility to the CO₂ compression, transport, and storage processes. This holistic approach reflects recent findings that emphasize the importance of including all indirect emissions to determine true net removal.
We hope that developers of CDR standards take note, as accurate certification schemes should aim to build trust—something that can only happen with precise and transparent data.
Case Study: Liquid-DAC in California vs. Solid-DAC in France
To illustrate how the Direct Air Capture Lifecycle Analysis Tool (DAC-LAT) supports decision-making, here are two real-world scenarios that highlight the impact of different technology choices, energy inputs, and regional settings on net CO₂ removal.
Case 1: Liquid Sorbent DAC in California (U.S. grids, natural gas with recapture)
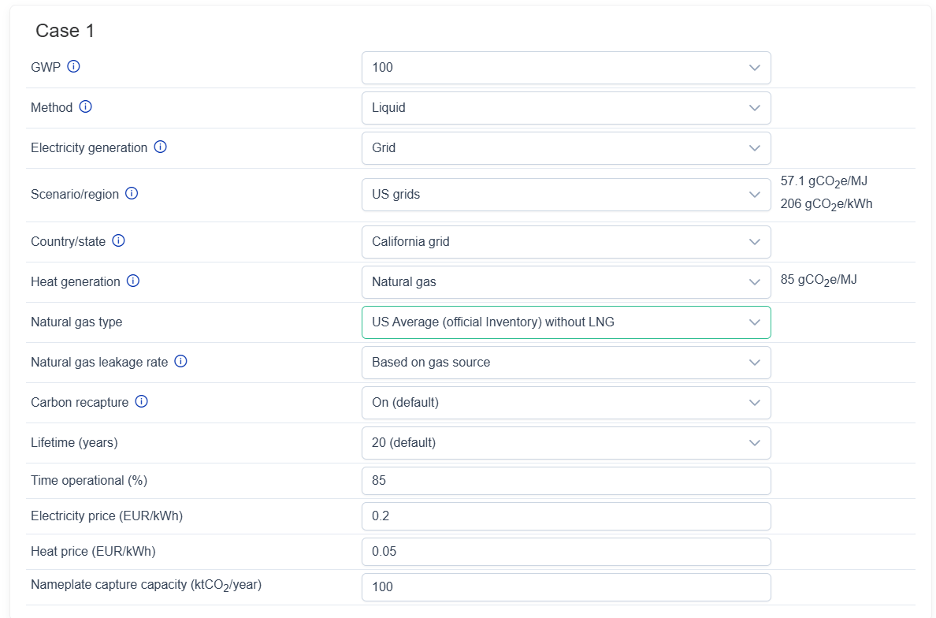
In this scenario, a liquid-based DAC facility operates in California, using grid electricity and heat from natural gas with carbon recapture. This means that CO₂ produced by the natural gas in the high-temperature sorbent regeneration process is also captured and stored along with the atmospheric CO₂.
Facility Specs:
- Capture capacity: 100 ktCO₂/year
- Operational time: 85% of the year
- Plant lifetime: 20 years
Key Findings:
| Energy Inputs | |
|---|---|
| Electricity | 1.23 MJ/kg CO₂ |
| Heat | 6.28 MJ/kg CO₂ |
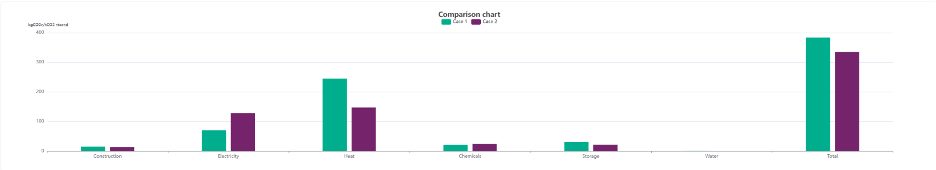
| Total Lifecycle Emissions | 383.2 gCO₂e per kg CO₂ stored |
| Largest Emission Sources | Heat (244.7 gCO₂e per kg CO₂), electricity (70.2), and chemicals (21.34) |
| Total CO₂ Stored | 109.57 ktCO₂/year, of which 85 ktCO₂/year is atmospheric CO₂ |
This case illustrates the emissions burden associated with fossil fuel-based heat, even with recapture.
- CO₂ and methane emissions from the natural gas supply chain contribute over 50% of the total life-cycle emissions.
Case 2: Solid Sorbent DAC in France (with grid electricity and heat from nuclear power)
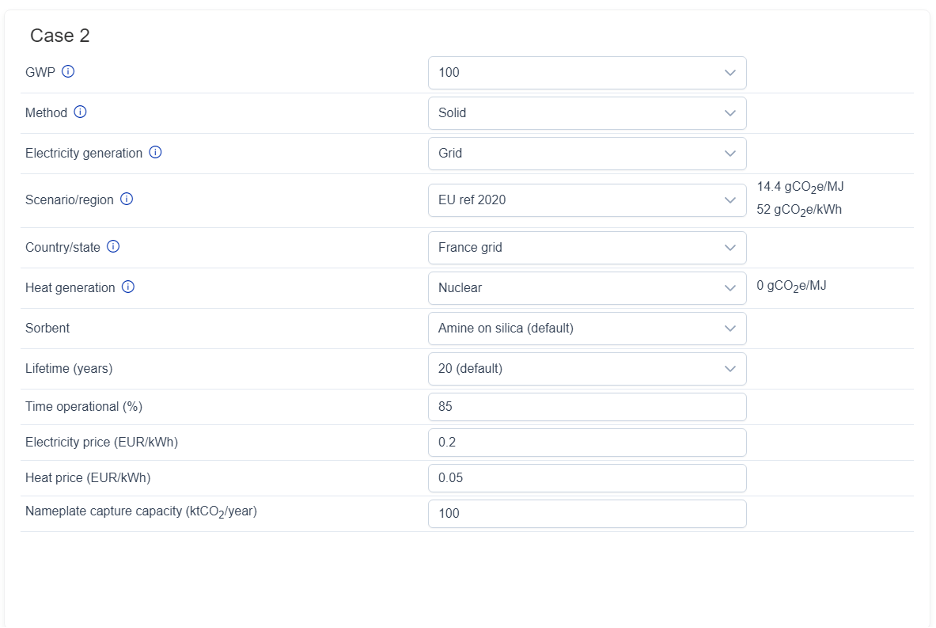
A second scenario models a solid-based DAC facility in France, using low-carbon grid electricity and drawing heat from a nuclear power plant. The basic case of silica-supported amines is selected here.
Facility Specs:
- Capture capacity: 100 ktCO₂/year
- Operational time: 85% of the year
- Plant lifetime: 20 years
Key Findings:
| Energy Inputs | |
|---|---|
| Electricity | 2.52 MJ/kg CO₂ |
| Heat | 11.9 MJ/kg CO₂ |
| Total Lifecycle Emissions | 79.66 gCO₂e per kg CO₂ stored |
| Largest Emission Sources | Chemicals (24), electricity (36.22), and storage (6.11) |
| Total CO₂ Stored | 85 ktCO₂/year |
This scenario highlights the benefit of low-carbon electricity sources (e.g., nuclear power) in minimizing lifecycle emissions.
- Emissions are nearly four times lower than in Case 1, underscoring how energy sourcing significantly influences DAC’s climate impact.
DAC‐LAT is designed to help decision-makers see the bigger picture: while a DAC facility can remove carbon, its effectiveness depends on multiple factors.
With limited time and resources, it's paramount to optimize DAC technology choices and facility placement.
We hope this tool can help by:
- Highlighting promising countries and regions for DAC deployment.
- Emphasizing lifecycle analysis in carbon removal certification standards.
Subscribe to the newsletter
Daily decarbonization data and news delivered to your inbox
Follow the money flow of climate, technology, and energy investments to uncover new opportunities and jobs.
Latest issues
-
Canada Nickel Just Buried CO₂ Before Mining Even Started
Inside This Issue ⛏️ Canada Nickel And UT Prove Mining Can Fight Climate Change 🛰️ OGCI And Carbon Mapper Team Up To Reduce Methane Emissions From The Oil And Gas Sector 🚛 RNG Continues To Lead As...
-
96% Pure H₂ Found Underground — Now What?
Inside This Issue 🧪 HyTerra's Kansas H₂ Could Power a Historic Industry First 🤝 Prime Minister Carney Secures Ambitious New Partnership With India Focused on Energy, Talent, and Technology Françai...
-
What Do Submarines Have to Do With Hydrogen?
Inside This Issue 🚢 Hyundai Pitches Hydrogen Transport Tied To Canada Submarine Bid 🧱 The LEGO Group Expands Its Portfolio Of Carbon Removal Solutions 🏆 SAF Pioneer LanzaJet Honored With RFA Indus...
Company Announcements
-
OGCI And Carbon Mapper Team Up To Reduce Methane Emissions From The Oil And Gas Sector
OGCI, Carbon Mapper collaboration combines public satellite methane data and science-driven strategy with industry-led engagement. Mitigating methane emissions is one of the fastest and most effec...
-
NEWPORT BEACH, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Clean Energy Fuels Corp. (NASDAQ: CLNE), the largest provider of the cleanest fuel for the transportation market, has announced a slew of deals with trucking...
-
MENLO PARK, Calif., March 4, 2026 /PRNewswire/ -- Mainspring Energy Inc. today announced that it has been awarded a contract by the United States Department of the Air Force (DAF) for a pilot progr...
-
Plug Power Welcomes Jose Luis Crespo as Chief Executive Officer
Crespo’s commercial and operational expertise positions Plug for disciplined growth and execution SLINGERLANDS, N.Y., March 03, 2026 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Plug Power Inc. (NASDAQ: PLUG), a global le...