
“Dirty Water, Clean Power”: New Tech Breakthrough Lets Electrolyzers Produce Hydrogen Without Needing Pure Water Sources
Published by Todd Bush on July 3, 2025
Researchers in China have developed a groundbreaking technique that allows proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolyzers to produce clean hydrogen from impure water, potentially reducing costs and expanding the technology's applicability in the quest for sustainable energy solutions.
IN A NUTSHELL
- 🌊 Researchers in China have developed a method that enables PEM electrolyzers to work with impure water, reducing costs.
- 🔬 The innovation involves creating an acidic microenvironment using Bronsted acid oxide to enhance electrolyzer performance.
- 💡 This breakthrough could significantly lower the cost of hydrogen production and facilitate broader deployment of the technology.
- 🌍 By making hydrogen production more accessible, this advancement supports global efforts to transition to clean energy solutions.
In the quest for sustainable energy, hydrogen stands out as a promising candidate. However, the challenge lies in producing clean hydrogen efficiently and economically. Traditional PEM electrolyzers demand ultrapure water, making the process costly and limiting its widespread adoption. Recently, a team of researchers in China has developed a groundbreaking approach that allows PEM electrolyzers to function with impure water, potentially revolutionizing the hydrogen production landscape. This innovation could significantly lower costs and enable broader deployment of hydrogen technology, marking a significant step forward in the global push for cleaner energy solutions.
Understanding the Challenges of Electrolyzers
Electrolysis, the process of splitting water molecules to produce hydrogen, is a well-established technology. Despite its potential, widespread adoption has been hindered by several challenges. Alkaline electrolyzers, which are the most common, fail to produce hydrogen pure enough for fuel cell applications. On the other hand, PEM electrolyzers offer high purity hydrogen but require ultrapure water, which is both expensive and resource-intensive to produce.
Impurities present in water can rapidly degrade PEM electrolyzers, making them unsustainable for large-scale applications without extensive water treatment. This requirement for high-purity water has presented a significant barrier to deploying these systems widely. However, by addressing this fundamental issue, researchers are opening new avenues for the practical use of hydrogen as a clean energy source.
Innovative Solutions: Creating Acidic Microenvironments
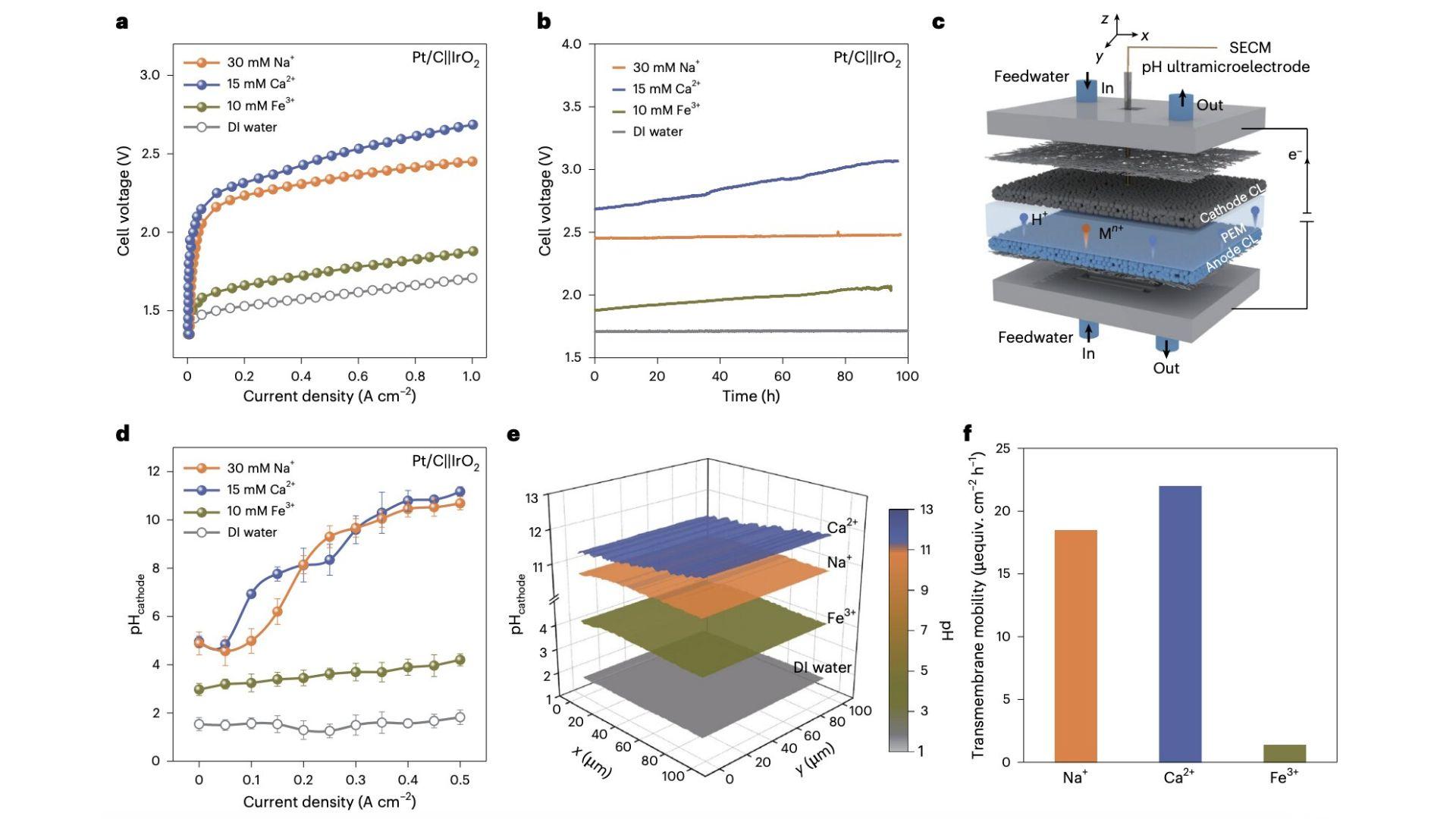
The breakthrough from Tianjin University and collaborating institutes involves creating an acidic microenvironment within the PEM electrolyzer. They achieved this by adding Bronsted acid oxide (MoO3-x) to the cathode. This addition acts as a catalyst, effectively lowering the pH in the immediate vicinity of the reaction, enhancing the electrolyzer’s performance even with impure water.
This technological advancement was verified through sophisticated methods such as pH ultramicroelectrode measurements and scanning electrochemical microscopy. The results were promising, showing that PEM electrolyzers could operate with tap water for over 3,000 hours, maintaining performance levels comparable to those using ultrapure water. This innovation not only reduces the need for costly water pretreatment but also extends the longevity and efficiency of the electrolyzers.
>> In Other News: H2SITE Secures EIC Accelerator Funding to Deploy a Flagship 1 TPD Ammonia Cracker Using Membrane Reactor Technology at a Port in North-West Europe
Implications for the Hydrogen Economy
The ability to use impure water in PEM electrolyzers could dramatically reduce the overall cost of hydrogen production. By minimizing the need for extensive water purification, the technology becomes more accessible and economically viable. This is particularly crucial for regions where water resources are limited or where water purification infrastructure is inadequate.
Moreover, this development aligns with global efforts to transition to cleaner energy sources. As the world seeks to reduce its carbon footprint, hydrogen offers a high-energy, zero-emission alternative. The ability to produce hydrogen more affordably could accelerate its adoption across various sectors, including transportation, industry, and energy storage, thus playing a pivotal role in combating climate change.
Future Prospects and Considerations
While the research is still in its early stages, the potential impact of these findings is substantial. By enabling PEM electrolyzers to function with less stringent water quality requirements, the path is paved for more flexible and scalable hydrogen production systems. This could lead to increased investment in hydrogen infrastructure and greater innovation in related technologies.
However, challenges remain. The long-term durability of these modified electrolyzers and their performance in diverse environmental conditions need further exploration. Additionally, the economic feasibility of widespread implementation must be thoroughly assessed to ensure that the benefits outweigh the costs. As we look to the future, one must ask: how will this innovation influence the trajectory of global energy policies and the broader adoption of hydrogen-based solutions?
Subscribe to the newsletter
Daily decarbonization data and news delivered to your inbox
Follow the money flow of climate, technology, and energy investments to uncover new opportunities and jobs.
Latest issues
-
This $4.1M Deal Could Change Carbon Capture's Playbook
Inside This Issue 🗜️ CarbonQuest Lands $4.1M Alberta Deal on Gas Compressors 🛡️ CADO, 123Carbon, and Assure SAF Registry Join Forces to Tackle SAF Integrity Gaps ✈️ ISCC, OMV, and Airbus Partner t...
-
Can Koloma Crack Iowa's Billion-Year-Old Secret?
Inside This Issue ⛏️ Iowa's Hydrogen Rush: Can Koloma Strike Gold Before Rules Kick In? ✈️ Bentley Commits to Use 100% Sustainable Aviation Fuel for Car Airfreight 🌬️ Minister Parrott Provides Upd...
-
$47M Just Poured Into This SAF Producer
Inside This Issue 💰 LanzaJet Announces $47M in New Capital and First Close of Equity Round at $650M Pre-Money Valuation 🚢 Maersk's Ethanol Bet Could Reshape U.S. Fuel Markets 🪨 Canada Nickel and t...
Company Announcements
-
Feedstocks are Perennial Grasses and other Renewable Biomass Sources FREDERICK, Md., Feb. 18, 2026 /PRNewswire/ -- Do you know why passenger and freight planes are not using renewable biofuel? It'...
-
Vancouver, British Columbia--(Newsfile Corp. - February 25, 2026) - Q Precious & Battery Metals Corp. (CSE: QMET) (OTC Pink: BTKRF) (FSE: 0NB) ("QMET" or the "Company") congratulates Quebec Inn...
-
Carbon Direct and C2X Announce Collaboration on Pioneering Forestry Residue-to-Biofuel Project
Collaboration on C2X’s Beaver Lake Biofuels project advances biomass carbon removal and storage as a scalable climate solution, transforming Louisiana’s forestry and sawmill residues into biofuel a...
-
Carbon Direct and C2X Announce Collaboration on Pioneering Forestry Residue-to-Biofuel Project
Collaboration on C2X’s Beaver Lake Biofuels project advances biomass carbon removal and storage as a scalable climate solution, transforming Louisiana’s forestry and sawmill residues into biofuel a...