
The Four Corners Carbon Storage Hub project is set to be a game-changer in carbon management, spearheaded by a collaborative effort between New Mexico Tech and key industry partners. With support from the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Fossil Energy and Carbon Management (FECM), this project aims to establish a large-scale carbon storage hub in the Four Corners region. The initiative highlights the growing importance of carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies in addressing climate change, all while benefiting local communities.
>> RELATED: DOE’s Push for Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Technologies to Drive Decarbonization
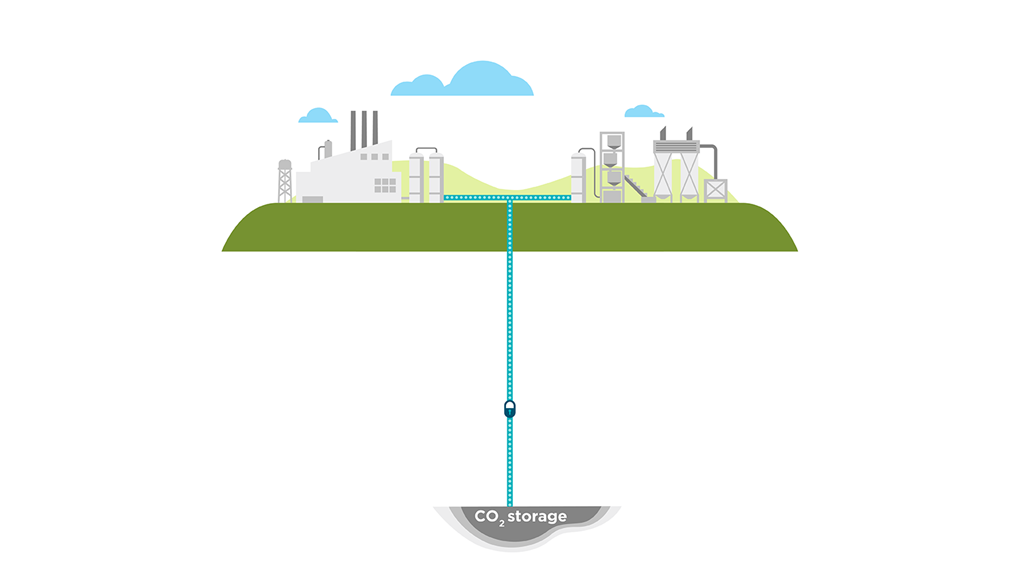
The Companies Driving the Project Forward
At the heart of the Four Corners Carbon Storage Hub are some of the most esteemed academic and industry players, led by New Mexico Tech. With its deep expertise in geology and engineering, New Mexico Tech is tasked with overseeing the project’s development, which involves conducting comprehensive site characterizations across the San Juan Basin.
This site will potentially store significant amounts of CO2, sourced mainly from the Four Corners Power Plant, which emits over 10 million metric tons of CO2 per year.
The project is bolstered by a collaboration with Enchant Energy, which is also focused on advancing CCS technology in the region. Together, these companies aim to transform the Four Corners region into a hub for carbon management, paving the way for cleaner energy production and long-term environmental benefits.
Dr. William Ampomah, a professor at New Mexico Tech and a key figure in the project, noted that "this initiative is crucial for ensuring that the local community, particularly the Navajo Nation, benefits from both the technological advancements and the job opportunities that come with it."
A Holistic Approach to Carbon Management
The Four Corners Carbon Storage Hub isn't just about technology; it’s about creating sustainable benefits for the surrounding communities.
One of the key objectives is to ensure that the project aligns with the needs of local populations, particularly those in the Navajo Nation, who will see direct benefits from the employment and energy produced by the project.
One of the central tasks of the project is site characterization, where the team will evaluate the geological feasibility of storing CO2 in underground formations.
The team will collect core samples, perform seismic surveys, and conduct fluid sampling to ensure the chosen sites are capable of storing large volumes of CO2 safely.
This in-depth research will help determine the overall capacity of the storage sites and confirm that the CO2 will be securely stored without leakage.
Dr. Robert Balch, Director of the Petroleum Recovery Research Center and project manager for the Four Corners project, explained that “this is not just about technology; it’s about working with the community and ensuring that they are part of this transition towards a sustainable future.”

>> In Other News: The World’s First Ship-to-ship Ammonia Transfer at Anchorage: “a Major Milestone to Decarbonize Shipping Fuel”
Community and Environmental Impact
The Four Corners Carbon Storage Hub is deeply committed to fostering community engagement and ensuring that local populations, particularly those in disadvantaged areas, are involved in the project’s development. This includes implementing Community Benefit Plans (CBPs) that address societal and environmental considerations and provide real benefits to local stakeholders.
Kelly Ror, a member of the carbon management engagement team, emphasized the significance of these plans: “Community Benefit Plans are designed to ensure that the benefits of this project are felt not just environmentally but socially and economically as well. We’re working closely with local labor and community stakeholders to ensure that these benefits are tangible and long-lasting.”
The project will also focus on creating high-quality jobs and investing in workforce development, particularly within the Navajo Nation. A major goal is to attract and train talent from the local communities, ensuring that they have access to the employment opportunities generated by the project.
Additionally, partnerships with local colleges and universities will play a vital role in providing the necessary education and training for community members to take part in the project.
Key Technical Milestones
Over the course of the project, several key technical milestones will be achieved. The primary focus will be on conducting site characterizations at three potential storage sites within the San Juan Basin.
The project will drill two new wells and reenter an existing well to collect core samples and perform fluid analyses. The data collected will help create detailed models predicting how CO2 will behave once injected into the subsurface.
These technical assessments are vital to obtaining the necessary permits from the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). The project will submit applications for UIC Class VI permits, which are required for CO2 injection wells. Two of the sites are located on Navajo Nation land, which falls under EPA Region 9, while the third site is on private land in EPA Region 6.
The project also includes developing a storage field development plan, outlining how the storage sites will be managed and maintained. This comprehensive plan will be essential for ensuring that the CO2 is stored securely over the long term, minimizing any environmental risks.
Economic and Social Benefits for the Navajo Nation
The Four Corners Power Plant and the associated mine are crucial to the Navajo Nation, accounting for approximately 42% of the Navajo Nation's general fund. The plant provides not only a stable energy source but also employment opportunities for the local community. Shutting down the plant could lead to job losses and a significant reduction in revenue for the Navajo Nation.
By developing the Four Corners Carbon Storage Hub, the project aims to secure the future of the power plant while also contributing to environmental sustainability. This ensures that local jobs are preserved and new opportunities are created in the growing field of carbon management. "Our role as scientists is to ensure that we find a home for the CO2," said Dr. William Ampomah.
Looking Forward
The Four Corners Carbon Storage Hub is a pivotal project for the region, combining cutting-edge carbon management technology with a strong focus on community engagement and environmental justice.
With the involvement of key industry players like New Mexico Tech and Enchant Energy, this initiative is not only setting a standard for carbon storage but also ensuring that the benefits reach the local communities, particularly within the Navajo Nation.
The commitment to developing a sustainable future while addressing local needs makes this project a model for future carbon management endeavors.
Subscribe to the newsletter
Daily decarbonization data and news delivered to your inbox
Follow the money flow of climate, technology, and energy investments to uncover new opportunities and jobs.
Latest issues
-
Sustaera's 3rd-Gen DAC Could Crack the $100/Ton Barrier
Inside This Issue 🧪 Sustaera's 3rd-Gen DAC Could Crack The $100/Ton Barrier ⚠️ Middle East Conflict Threatens To Derail The Region's Carbon Capture Boom 🌿 Svante And Integrated Packaging Company A...
-
PJM's AI Power Crisis Just Got a 250MW Hydrogen Answer
Inside This Issue ⚡ Plug Power Plans Hydrogen Offering in Top US Power-Grid Auction 🪨 Underground CO2 Storage, X-Rays Reveal Carbon Capture Capacity of Volcanic Rocks 🍁 Swiss Carbon Capture Compan...
-
One Montana Site Could Supply Half of North America's SAF
Inside This Issue ✈️ Montana's $1.44B Bet on Aviation Fuel Enters Final Stretch 🌍 Carbon Removal Coalition Forms With Goal of Attracting $100-Million in Project Investments 🤝 Prime Minister Carney...
Company Announcements
-
Trafigura’s Morgen Energy Reaches Final Investment Decision for 20MW Green Hydrogen Project in Wales
Trafigura, a market leader in the global commodities industry, today announces that its wholly-owned subsidiary, MorGen Energy, has approved the final investment decision (FID) to begin constructio...
-
Chevron Lummus Global Expands Portfolio with Fischer-Tropsch Liquids Upgrading Solutions
Expansion strengthens hydroprocessing portfolio with proven technologies for upgrading FT derived liquid feedstock Chevron Lummus Global (CLG) announced the addition of Fischer-Tropsch (FT) liquid...
-
Ballard Announces Commercial Agreement With New Flyer For 50 MW Of Fuel Cell Bus Engines
VANCOUVER and WINNIPEG, CANADA – Ballard Power Systems (NASDAQ:BLDP; TSX:BLDP) today announced reaching a commercial agreement with New Flyer, a subsidiary of NFI Group Inc., (“NFI”; TSX:NFI; ), a ...
-
The joint venture will demonstrate H2Pro's DWE technological ability to operate directly on solar-pv renewable power; scaling from an initial 5 MW system toward a 50 MW RFNBO facility SEVILLE, Spa...