
Global CO₂ levels just hit a record high, 424 parts per million.
The clock is ticking.
Direct air capture (DAC) once sounded like sci-fi, but it’s quickly becoming one of the most ambitious bets in climate tech. Backed by major players and billions in funding, DAC is now scaling from pilot projects to industrial reality.
The concept of pulling carbon dioxide directly from the atmosphere once seemed like science fiction. Today, direct air capture (DAC) technology is moving from pilot projects to commercial-scale operations, driven by technological breakthroughs, substantial funding, and ambitious government backing. While challenges remain, the industry is demonstrating that large-scale atmospheric carbon removal may be achievable within this decade.
>> RELATED: Scaling Smarter: Climeworks and Svante Set New Bar for Direct Air Capture
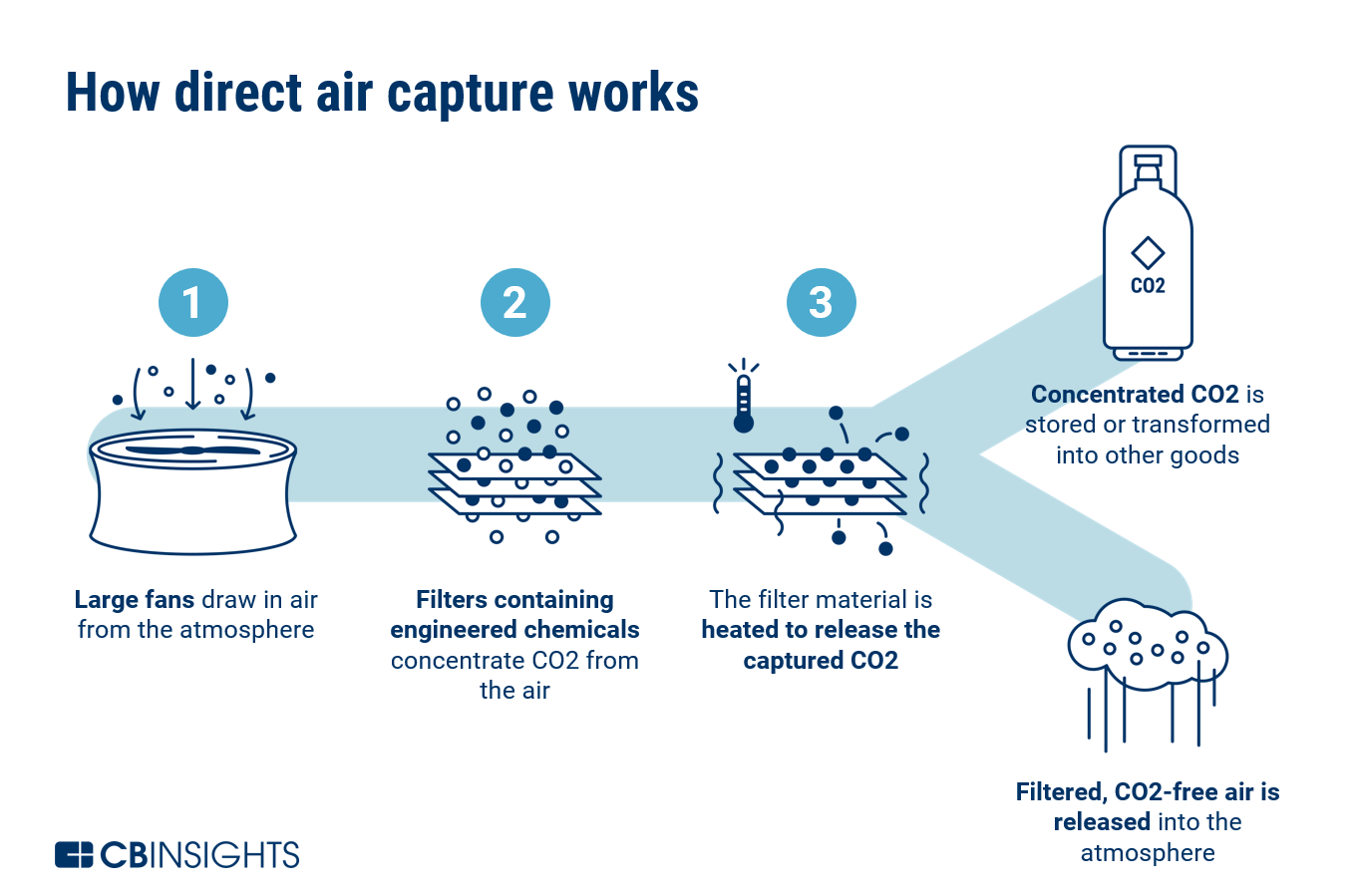
Breakthrough Technologies Driving Efficiency Gains
The DAC industry is experiencing significant technological advances that address its primary obstacle: energy consumption. Traditional DAC systems require substantial energy to operate, limiting their climate benefits and commercial viability.
Climeworks, a Swiss company that has operated the world's largest DAC facility since 2021, recently announced its Gen 3 technology developed with Svante. This new system uses structured adsorbents that promise to reduce energy consumption by 50% while doubling CO₂ capture capacity compared to current technology. Jan Wurzbacher, Climeworks' Co-CEO, noted that the technology has been "engineered for real-world conditions and real-world impact."
The innovation extends beyond energy efficiency. Skytree is developing decentralized DAC systems designed for localized deployment. Their Stratus system was recently selected for a Power-to-X pilot project with Forschungszentrum Jülich, where captured CO₂ will be converted into green methanol, demonstrating how atmospheric carbon can become feedstock for sustainable fuels and chemicals.
Aircapture raised $50 million in Series A funding to deploy modular DAC systems directly at industrial sites. This approach eliminates transportation costs and emissions while providing immediate CO₂ supply for companies seeking to reduce their carbon footprint or produce carbon-neutral products.
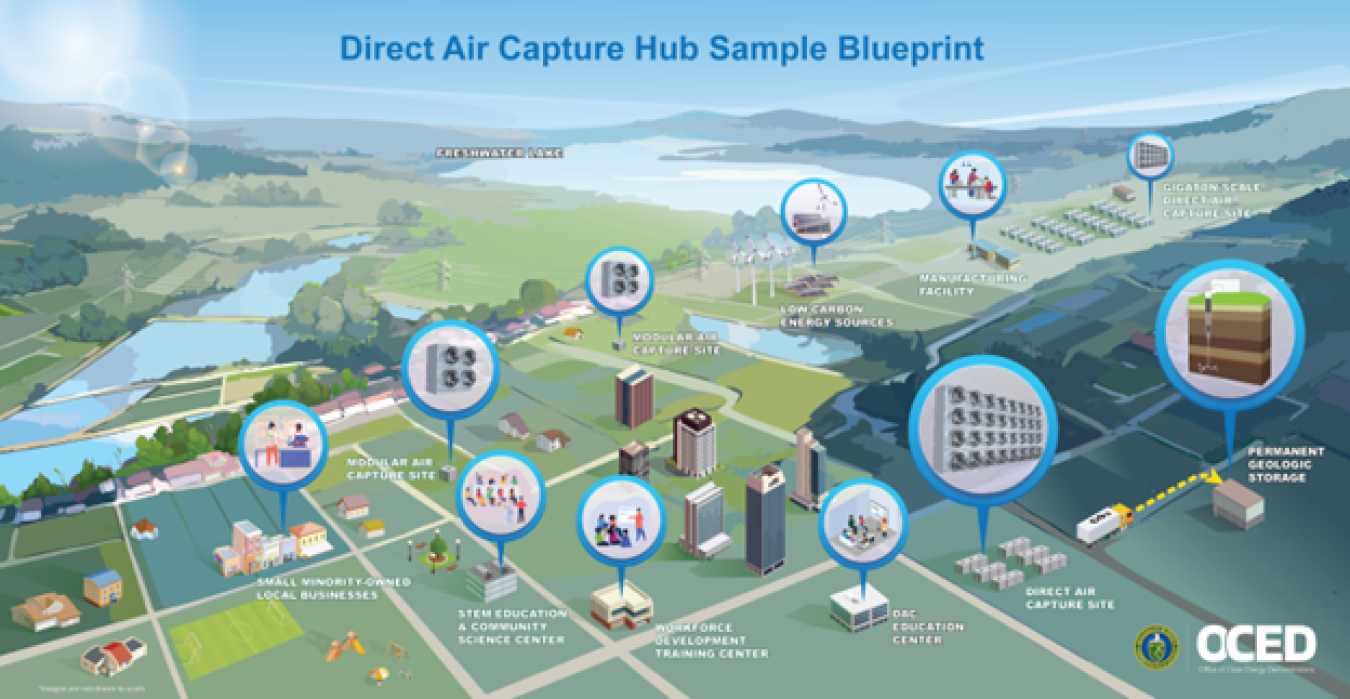
North America's Hub Strategy: Scaling to Gigatons
The United States is positioning itself as a global leader in DAC deployment through the Department of Energy's Regional Direct Air Capture Hubs program. This $3.5 billion initiative aims to establish multiple large-scale facilities capable of removing millions of tons of CO₂ annually.
Two major hubs are taking shape:
South Texas DAC Hub: Led by 1PointFive (Occidental Petroleum's subsidiary) in partnership with Carbon Engineering, this facility aims to remove up to 1 million tons of CO₂ per year when fully operational.
Project Cypress (Louisiana): This hub brings together Battelle, Climeworks, and Heirloom Carbon Technologies to establish a comprehensive DAC ecosystem in the Gulf Coast region.
CarbonCapture Inc. is developing another hub in Northwest Louisiana that uniquely integrates sustainable aviation fuel production with carbon removal. “We’re extremely grateful for the DOE’s support in moving our TA‑2 to Louisiana,” said Adrian Corless, CEO of CarbonCapture Inc. “By incorporating critical learnings, particularly in power sourcing and site selection, we’re accelerating the deployment of our cutting‑edge DAC technology in a state that has already demonstrated its commitment to advancing climate solutions.”
These hubs represent a crucial test of whether DAC can scale from today's thousands of tons annually to the millions, and eventually billions, of tons needed to meaningfully impact atmospheric CO₂ levels.
>> In Other News: URI Taking Part in International Research to Measure Hydrogen Emissions
Economic and Infrastructure Challenges
Despite technological progress, significant hurdles remain. Current DAC costs range from $200-600 per ton of CO₂, far above the $100-150 per ton that many analysts consider necessary for widespread deployment. The industry relies heavily on government incentives, including the U.S. 45Q tax credit that provides up to $180 per ton for permanently stored CO₂.
Infrastructure development presents another challenge. Large-scale DAC requires:
Abundant clean energy sources to avoid creating net emissions
CO₂ transport infrastructure, including pipelines and storage facilities
Class VI injection wells for permanent geological storage
Skilled workforce and supply chain development
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has approved only two Class VI wells nationwide, though dozens more are in various stages of permitting. The Department of Energy's Carbon Storage Atlas indicates substantial geological storage capacity exists, but developing this infrastructure will require significant time and investment.
Market Drivers and Future Outlook
Several factors are driving DAC development forward:
- Corporate demand: Companies including Microsoft, Google, and Meta have purchased DAC credits as part of net-zero commitments, creating early market demand despite high costs.
“We are excited about this landmark agreement for Direct Air Capture, which is a result of Microsoft’s leadership in carbon removal and focus on building a more sustainable future.”
— Michael Avery, President and General Manager of 1PointFive, on Microsoft’s purchase of
500,000 metric tons of DAC carbon removal credits over six years—the largest direct air capture deal to date.
Policy support: Beyond the U.S., governments in Canada, the UK, and EU are developing frameworks to support DAC deployment.
Voluntary carbon markets: While still nascent, demand for high-quality carbon removal credits is growing among companies seeking to offset emissions.
Integration opportunities: DAC facilities can be co-located with renewable energy projects, industrial facilities, or geological storage sites to reduce costs and improve economics.
The Path to Scale
Industry experts suggest that achieving meaningful climate impact will require removing 1–10 billion tons of CO₂ annually by 2050. Current global DAC capacity is approximately 10,000 tons per year, highlighting the enormous scale-up challenge ahead.
Success will likely depend on continued technological innovation, supportive policy frameworks, and the development of robust carbon markets. The next five years will be critical in determining whether today's promising pilot projects can evolve into the industrial-scale infrastructure needed to meaningfully address climate change.
The direct air capture industry stands at a pivotal moment. While significant challenges remain, the combination of technological breakthroughs, substantial funding, and policy support suggests that large-scale atmospheric carbon removal may transition from possibility to reality within this decade. The question is no longer whether DAC will work, but whether it can scale fast enough to make a meaningful difference in our fight against climate change.
The direct air capture industry stands at a pivotal moment. While significant challenges remain, the combination of breakthroughs, funding, and policy support suggests large-scale carbon removal could finally go mainstream.
If DAC doesn’t scale, the planet pays the price.
Subscribe to the newsletter
Daily decarbonization data and news delivered to your inbox
Follow the money flow of climate, technology, and energy investments to uncover new opportunities and jobs.
Companies
-
1
1pointFive
z
-
Occidental Petroleum Corporation
OXY
-
C
Carbon Engineering
-
C
Climeworks
-
Svante
-
-

CarbonCapture Inc
-

Skytree
-
Latest issues
-
Sustaera's 3rd-Gen DAC Could Crack the $100/Ton Barrier
Inside This Issue 🧪 Sustaera's 3rd-Gen DAC Could Crack The $100/Ton Barrier ⚠️ Middle East Conflict Threatens To Derail The Region's Carbon Capture Boom 🌿 Svante And Integrated Packaging Company A...
-
PJM's AI Power Crisis Just Got a 250MW Hydrogen Answer
Inside This Issue ⚡ Plug Power Plans Hydrogen Offering in Top US Power-Grid Auction 🪨 Underground CO2 Storage, X-Rays Reveal Carbon Capture Capacity of Volcanic Rocks 🍁 Swiss Carbon Capture Compan...
-
One Montana Site Could Supply Half of North America's SAF
Inside This Issue ✈️ Montana's $1.44B Bet on Aviation Fuel Enters Final Stretch 🌍 Carbon Removal Coalition Forms With Goal of Attracting $100-Million in Project Investments 🤝 Prime Minister Carney...
Company Announcements
-
Ballard Announces Commercial Agreement With New Flyer For 50 MW Of Fuel Cell Bus Engines
VANCOUVER and WINNIPEG, CANADA – Ballard Power Systems (NASDAQ:BLDP; TSX:BLDP) today announced reaching a commercial agreement with New Flyer, a subsidiary of NFI Group Inc., (“NFI”; TSX:NFI; ), a ...
-
The joint venture will demonstrate H2Pro's DWE technological ability to operate directly on solar-pv renewable power; scaling from an initial 5 MW system toward a 50 MW RFNBO facility SEVILLE, Spa...
-
Lufthansa Cargo and CEVA Logistics Expand SAF Cooperation
Lufthansa Cargo is consistently advancing the use of Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) together with customers and partners. The focus is on a strategic approach based on three-year framework agreeme...
-
The Containerized, Transportable System by AIRCO™ (formerly Air Company) is Supported Through an 8-Figure AFWERX STRATFI Award with Funding from the U.S. Air Force NEW YORK--(BUSINESS WIRE)--AIRCO...