
Construction crews are now in the ground in West Terre Haute, Indiana, marking a turning point for one of the Midwest's most ambitious low-carbon ammonia projects. Samsung E&A officially broke ground on January 7, 2026, kicking off what's expected to become a cornerstone of America's clean energy infrastructure.
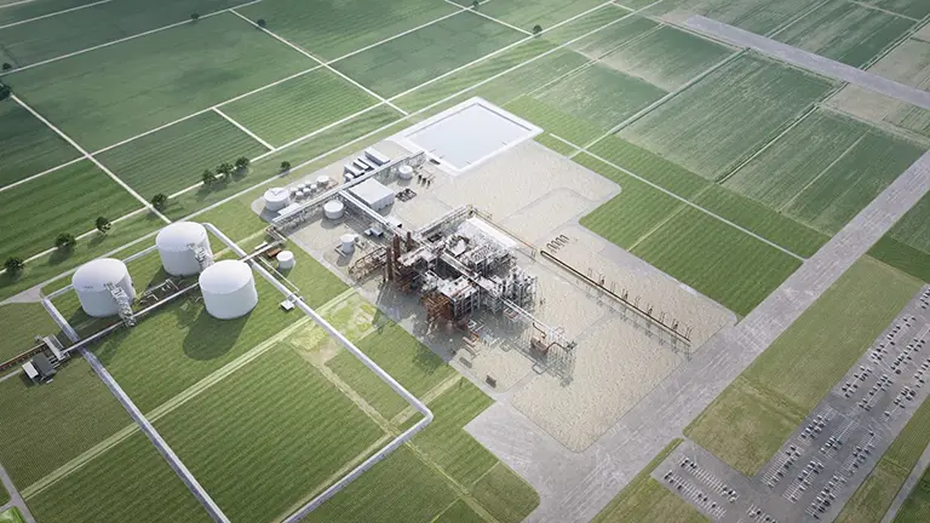
The facility, developed by Wabash Valley Resources, will convert petroleum coke into low-carbon ammonia while capturing roughly 1.67 million tons of CO2 annually. That's equivalent to taking over 360,000 cars off the road every year.
>> RELATED: $400M Bet on Blue Ammonia: Industry Giants Push Carbon Capture in Louisiana
What Makes This Project Different
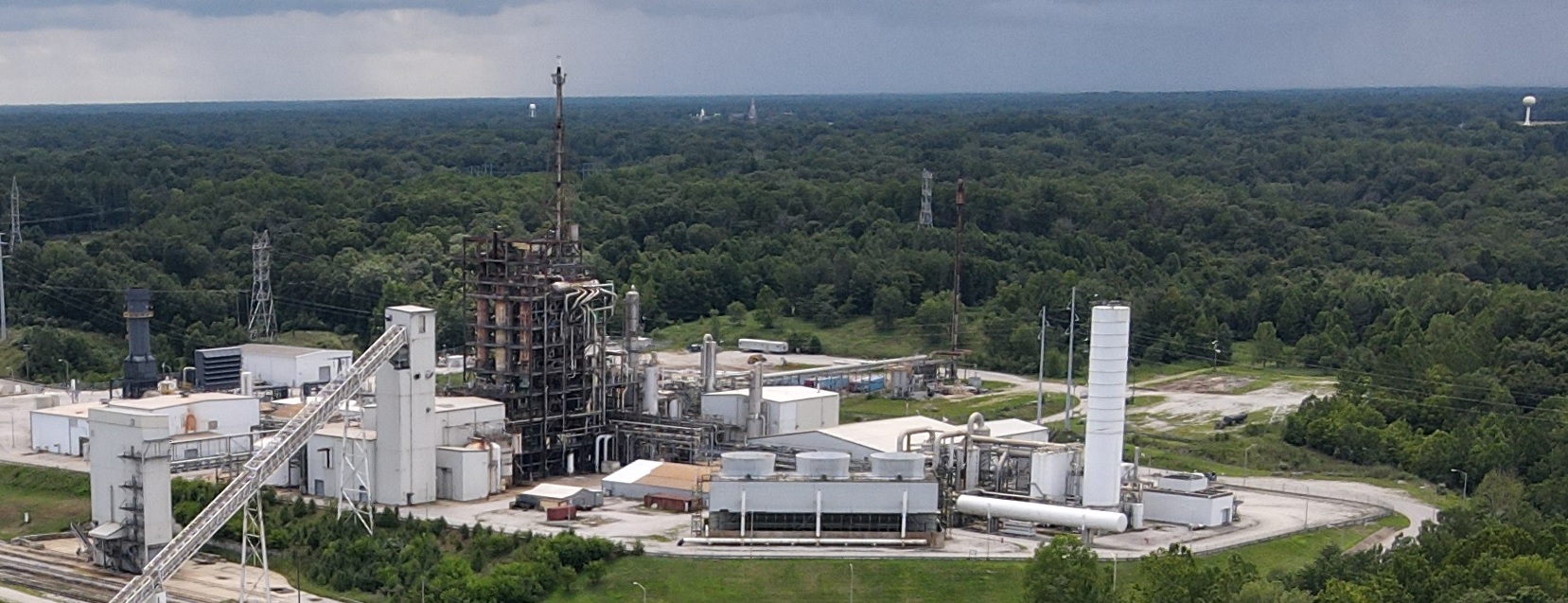

Unlike traditional ammonia production that relies heavily on natural gas reforming, the Wabash project takes a different path. It uses gasification technology to convert petroleum coke, a refinery byproduct, into synthesis gas. That syngas then becomes the feedstock for ammonia production.
The real innovation here is the integrated carbon capture system. Instead of releasing CO2 into the atmosphere, the facility will capture it and sequester it underground in deep geological formations.

A snapshot of the major low-carbon ammonia production facility project underway in West Terre Haute, Indiana, highlighting its significant investment and environmental goals.
Samsung E&A's Growing Clean Energy Footprint
This project isn't Samsung E&A's first foray into low-carbon ammonia. The South Korean engineering giant has been steadily building its portfolio in the decarbonization space, securing contracts across hydrogen production, sustainable fuels, and carbon capture.

"We are committed to delivering world-class engineering solutions that support the global transition to cleaner energy. Low-carbon ammonia represents a critical pathway for decarbonizing heavy industries."
Hong Namkoong, President and CEO, Samsung E&A
The company's expertise in complex energy projects makes it a natural fit for the Wabash facility. Managing the integration of gasification, ammonia synthesis, and carbon capture requires deep technical know-how and project management capabilities.
>> In Other News: Buckeye Gives Final Support to Rezone Nikola Property for Hydrogen Huba
Why Low-Carbon Ammonia Matters
Ammonia isn't just for fertilizers anymore. It's emerging as one of the most promising hydrogen carriers for long-distance energy transport. Countries like Japan and South Korea are already investing heavily in ammonia co-firing for power generation as they work to decarbonize their electricity grids.
The chemistry is straightforward. Ammonia can be cracked back into hydrogen at the destination. Unlike hydrogen, which requires extreme cooling, ammonia uses existing shipping infrastructure.
The U.S. is positioning itself as a major exporter in this space. Projects like Wabash Valley join a growing list of clean ammonia facilities coming online across the Gulf Coast and Midwest.

"Low-carbon ammonia is poised to become one of the most important energy carriers of the next decade. The economics are improving rapidly as carbon capture costs decline."
Hydrogen Council, Global Hydrogen Compass 2025 Report
The Policy Tailwind
Federal incentives are playing a big role. The 45Q tax credit offers up to $85 per ton for captured CO2 that's permanently sequestered. For a facility capturing 1.67 million tons annually, that translates to potential credits exceeding $140 million per year.
Indiana has also been working to attract carbon storage and clean energy investments. The state's central location and existing industrial infrastructure make it an attractive base for projects targeting both domestic and international markets.
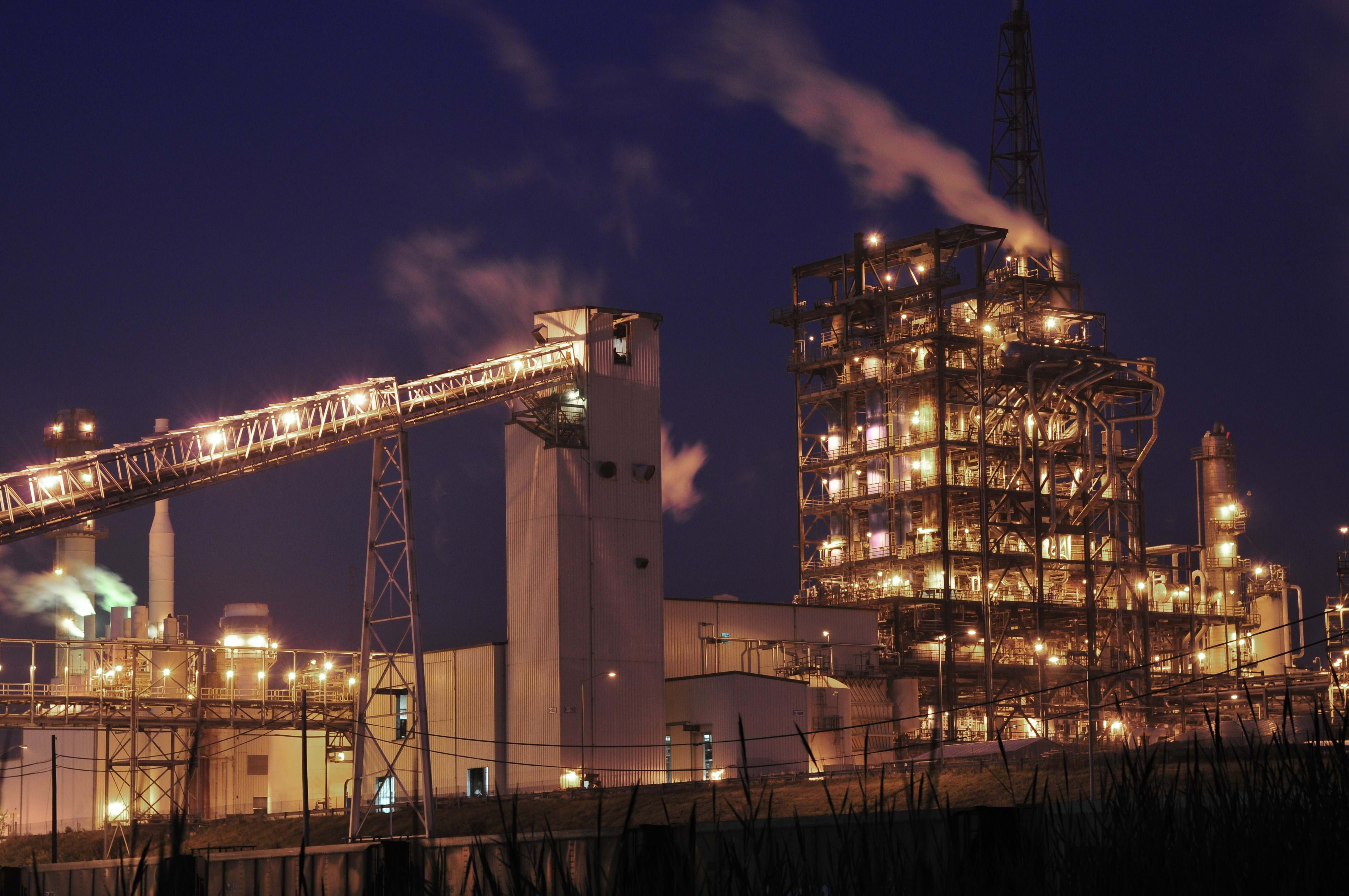

Building Momentum in the Midwest
The Wabash project adds to a wave of carbon capture investments sweeping through the heartland. Unlike the Gulf Coast, which has dominated headlines with mega-scale blue hydrogen and ammonia announcements, the Midwest is carving out its own niche.
What sets this region apart is access to different feedstocks and geological storage. The Illinois Basin, which extends beneath Indiana, offers significant CO2 sequestration potential that developers are just beginning to tap.
Indiana's industrial legacy also plays a role. The state has refining and chemical manufacturing infrastructure that can supply feedstocks like petroleum coke. Instead of treating petcoke as a waste product, facilities like Wabash Valley convert it into something valuable while capturing the carbon that would otherwise be released.
What Comes Next
The construction phase is expected to create hundreds of jobs in the region, with operations adding permanent positions once production begins.
For the broader industry, this groundbreaking sends a clear signal. Low-carbon ammonia isn't just a concept on paper. It's happening now, with real capital flowing into projects that combine proven technology with carbon management solutions.
The question is no longer whether these facilities can be built. It's how fast supply can scale to meet growing global demand.
Subscribe to the newsletter
Daily decarbonization data and news delivered to your inbox
Follow the money flow of climate, technology, and energy investments to uncover new opportunities and jobs.
Latest issues
-
Can Koloma Crack Iowa's Billion-Year-Old Secret?
Inside This Issue ⛏️ Iowa's Hydrogen Rush: Can Koloma Strike Gold Before Rules Kick In? ✈️ Bentley Commits to Use 100% Sustainable Aviation Fuel for Car Airfreight 🌬️ Minister Parrott Provides Upd...
-
$47M Just Poured Into This SAF Producer
Inside This Issue 💰 LanzaJet Announces $47M in New Capital and First Close of Equity Round at $650M Pre-Money Valuation 🚢 Maersk's Ethanol Bet Could Reshape U.S. Fuel Markets 🪨 Canada Nickel and t...
-
Kita's $29M Bet Signals Carbon Insurance Is Here
Inside This Issue 🛡️ Kita's $29M Bet Signals Carbon Insurance Is Here 🏗️ CCI BioEnergy Selects Arcadis As Design-Engineer Partner Under Master Service Agreement 🤝 Tapestry and Climeworks Announce ...
Company Announcements
-
Climeworks Establishes Canadian Headquarters in Calgary
Calgary, Alberta, February 20, 2026 — Climeworks, a global leader in commercial carbon removal, has established its Canadian headquarters at Calgary’s ETC, one of Alberta’s leading hubs where start...
-
MIAMI, Feb. 24, 2026 /CNW/ - Power Sustainable Infrastructure Credit ("PSIC") recently closed an $85M senior secured financing for Sagepoint Energy ("Sagepoint"), a vertically integrated renewable ...
-
HALIFAX, NS, Feb. 24, 2026 /CNW/ - The Nova Scotia Salmon Association (NSSA) is celebrating a significant advancement in climate action and watershed restoration as Royal Bank of Canada purchases a...
-
Honeywell International: Process Technology to Help Verso Energy Accelerate eSAF Production
CHARLOTTE, N.C., Feb. 24, 2026 - Honeywell today announced that Verso Energy, an integrated energy company focused on producing low-carbon molecules, will use Honeywell UOP's eFiningTM methanol-to-...